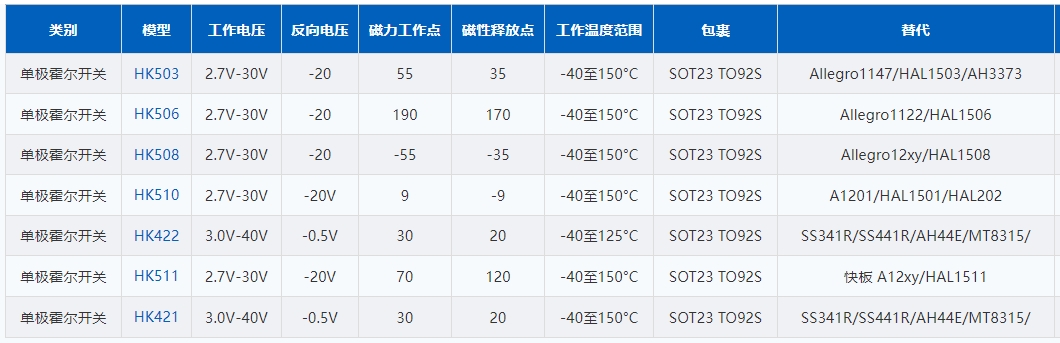
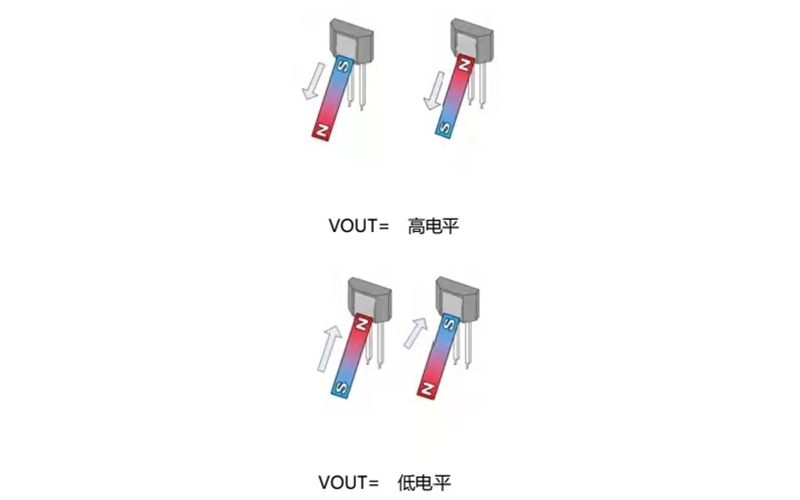
The typical working principle of a unipolar Hall switch:
Hall element: The core component of a Hall switch is a Hall element, usually a small piece of semiconductor material through which current flows. When a magnetic field is applied perpendicular to the Hall element, it generates a voltage difference between its terminals.
Threshold sensing: Single pole Hall switches are designed to respond to specific magnetic field polarities, north (N) or south (S). They are sensitive to the presence or absence of magnetic fields of that polarity.
Switch output: The output of a Hall switch is binary, which means it is in an "on" or "off" state, depending on whether a magnetic field of a specified polarity exists. When the magnetic field reaches a certain strength (usually a threshold level), the Hall switch will change its output state.
Single pole Hall switches are commonly used in various applications, such as proximity sensors, position sensors, speed sensors, and brushless DC motor control. They provide digital output signals that can be easily connected to microcontrollers and other digital electronic devices for control and automation purposes. The threshold level and sensitivity of Hall switches can usually be adjusted to meet specific application requirements.