6 methods for current detection - Weikewei - professional FAE guidance for selection
High precision current sensors are key to improving the efficiency of motor drive closed-loop control systems. In this article, the editor summarizes the advantages and disadvantages of different isolation current sensing methods and lists some typical applications of them.
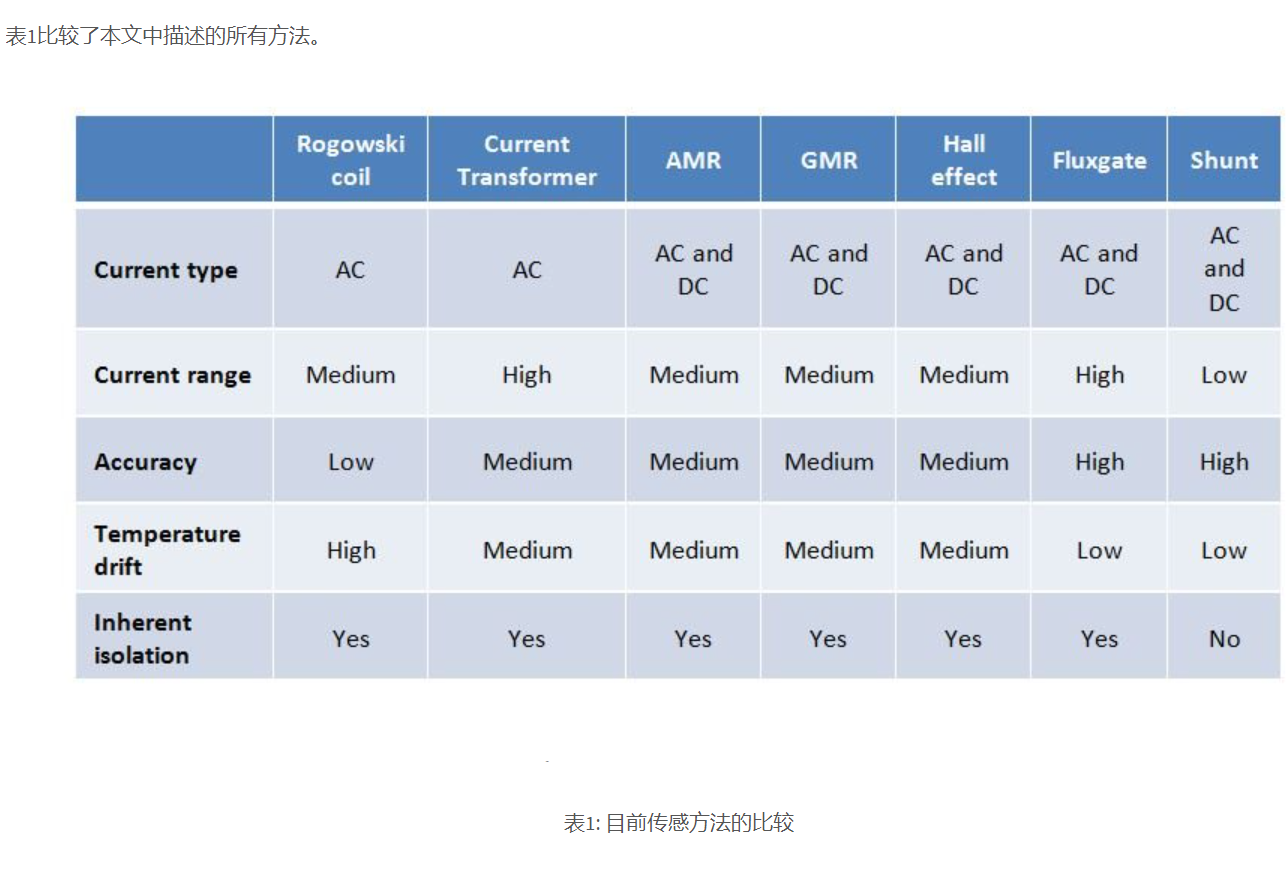
1. The shunt resistor is widely used in industrial applications, providing relatively high accuracy during low-temperature drift. However, the power consumption caused by their inherent resistance limits their use. In applications with high common mode voltage, parallel resistors require isolated amplifiers like AMC1200, or for the best performing systems, isolated delta sigma modulators like AMC1304L05 are needed. This device provides a low input voltage range of ± 50mV, allowing you to use smaller resistors for shunt without affecting performance.
2. The Rogowski coil only measures alternating current and wraps around the conductor where the distributed current is sensed. The voltage they provide is proportional to the rate of change of the alternating current, so an integrator is required before processing with an analog-to-digital converter circuit (ADC). Rogowski coils are suitable for retrofit applications as they can be installed around conductors without interrupting the current. They do not use metal cores, so the mechanical tolerances of positioning both affect and limit the achievable accuracy. For the same reason, they are unsaturated and therefore used in high current applications. Their low inductance allows for the use of high conversion rates in the system.
In a current transformer (CT), the primary AC current generates a magnetic field in the magnetic core. This magnetic field induces a proportional current in the secondary winding. A load resistor is required to convert the current into a voltage signal for further processing in the ADC. The accuracy of Ct depends on the set mechanical tolerances, ingredient accuracy, and temperature drift of the magnetic core. The saturation of the magnetic core limits the dynamic range of CT. On the other hand, specialized design allows you to customize CT for specific use cases. Current transformers are widely used for current detection in power systems.
4. The resistance of a magneto resistive sensor varies with the presence of a magnetic field, direct current, or alternating current. Magnetic resistance sensors have a small volume and are typically used for position and angle sensing. For low current applications that do not require high precision, they are cost-effective alternatives. According to the materials used, you can choose two types of magneto resistive sensors: a. Anisotropic Magnetoresistance Effect (AMR), which uses ferromagnetic materials where the magnetic field affects the resistance. The resistance change is very small, so the Wheatstone bridge is commonly used to detect b. The sensor relies on the significant influence of the magnetic field on the resistance of the structure composed of alternating ferromagnetic layers and non giant magnetoresistance effect layers. However, there is no free lunch in the world - compared to magnetic resonance sensors, the production process is more complex and expensive
5. The voltage signal transmitted by the Hall effect sensor is proportional to the AC or DC magnetic field. They themselves are noise, and the voltage level is highly dependent on temperature. You can address these two limitations by using smart excitation methods, such as the method used by DRV411 sensor signal conditioning integrated circuits (ICs). Hall sensors can be used for open-loop applications without requiring high precision levels. To improve accuracy, it is best to use a closed-loop approach, which includes Hall sensors, magnetic cores with compensating windings, and signal conditioning circuits typically in the form of complete modules. Closed loop modules can be used for a wide range of accuracy, current and cost levels. Other examples of Hall effect sensors include the DRV5000 series.
6. The flux gate sensor provides the highest level of sensitivity, the widest dynamic range, and the lowest noise and temperature drift performance compared to other current sensing methods. The design of external flux gate sensors is complex and requires low mechanical tolerances; Only a few manufacturers in the world provide flux gate sensor modules. Texas Instruments recently announced DRV421, the industry's first fully integrated flux gate sensor with all required signal conditioning functions for closed-loop DC and AC applications. With magnetic cores and compensation coils, this solution can easily manufacture high-precision and low-level (leakage) current modules.