How does a current sensor work- Weikewei - detection accuracy up to 0.5%
When current passes through a conductor, it generates a proportional magnetic field around the conductor. Current transformers use this magnetic field to measure current flow. If a current transformer is used to measure alternating current, induction technology is usually used. Alternating current changes the potential, causing the magnetic field to continuously collapse and expand. In AC current sensors, wires are wound around the magnetic core. The magnetic field generated by the current through the conductor induces a certain proportion of current or voltage in the wires inside the current sensor. Then, the sensor outputs a certain voltage or current, and the instrument connected to the sensor can read these voltages or currents and convert them into the amount of current flowing through the conductor. For example, when the current through the conductor is 400A, there can be a current transformer that outputs 333mV (333mV is a commonly used output for CT). Once you configure your instrument to read 400A when it receives a 333mV input, it will be able to calculate how much ampere flow is received through the conductor based on what input. The working principle of DC current sensors is similar, but they rely on Hall effect technology to operate.
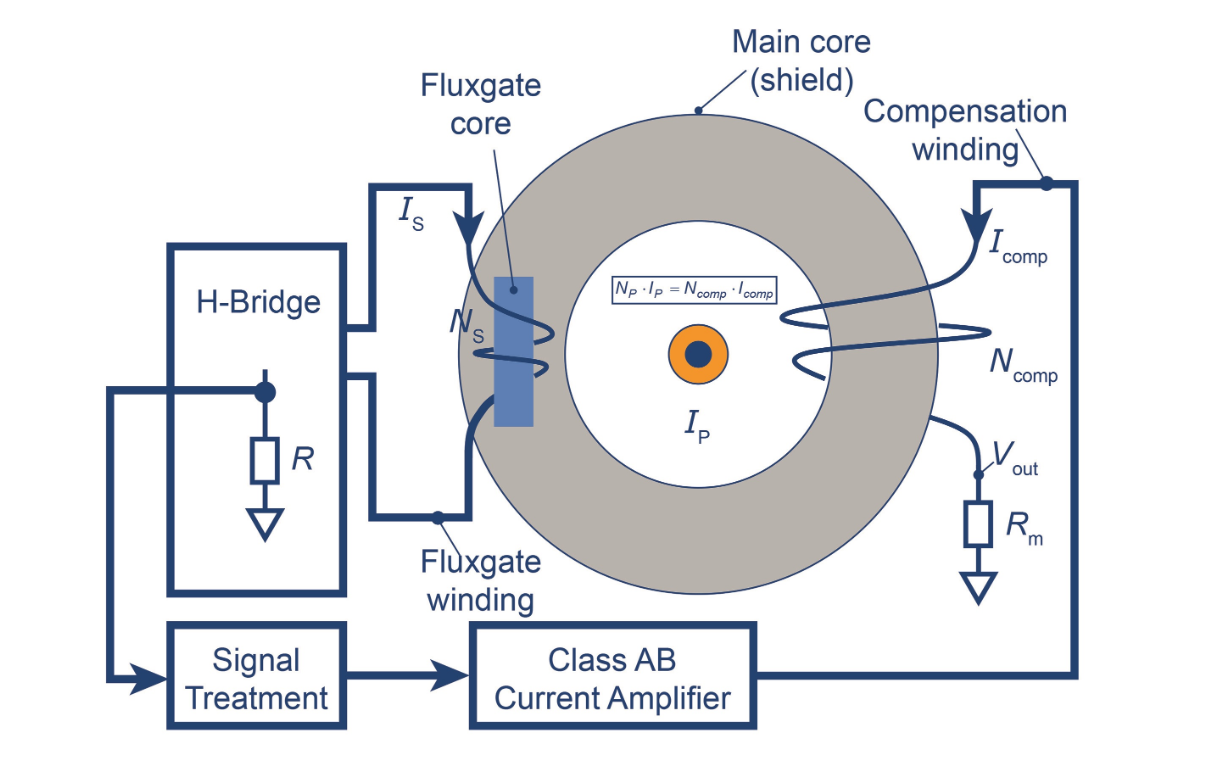
Current transformers can increase or decrease voltage, as well as maintain a constant current. Sensors that boost or buck current are usually referred to as transformers. Sensors typically consist of two coils. The coil through which current passes is called the primary winding, and the coil that induces voltage is called the secondary winding. For many of the current transformers we sell at Aim Dynamics, the conductor of the CT is installed as the primary winding, and the secondary winding is inside the transformer. The core of the secondary winding wrapping depends on the design and processing of the sensor.The turns ratio of a transformer is the number of turns of the secondary winding divided by the number of turns of the primary winding. This ratio determines whether the voltage of the transformer increases or decreases. The ratio of secondary voltage to primary voltage is equal to the turns ratio, as shown in the equation. Therefore, when the number of turns of the secondary winding is greater than that of the primary winding, the voltage of the secondary winding is higher, and it is a step-up transformer. The situation with current is exactly the opposite, where the ratio of secondary current to primary current is equal to the reciprocal of the turns ratio.