Working principle of Hall effect current sensor - Weikewei - Professional FAE guidance
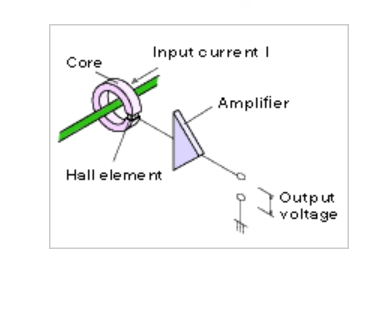
Hall effect sensors, or DC current sensors, are capable of measuring both AC and DC currents. The Hall effect sensor consists of a core, Hall effect devices, and signal conditioning circuits. Their operation is based on the Hall effect.
The Hall effect is a phenomenon discovered by Edwin Hall in 1879. When current passes through a conductor, a magnetic field is generated. If this conductor is located in another magnetic field, the magnetic field generated when electrons pass through the conductor will interact with the external magnetic field, causing the electrons to move to one side of the conductor. This generates a voltage on the conductor, which is proportional to the current flowing through the conductor and can be measured. A more in-depth description of the Hall effect can be found here.
Is there a difference between current transformers, current sensors, and current sensors?
Technically, yes, but these terms are usually interchangeable. These devices are all used to measure current and operate based on the same principle, but there are significant technical differences between them, which is worth noting. Technically speaking, a current transformer steps down the current to enable effective and safe monitoring, while a current sensor is a universal term for devices that sense and measure current. Sensors convert one input into another output. For example, they can convert AC signals into DC signals. However, all of these devices work similarly to measuring current and producing an output that can be read by an energy meter.