Why must the secondary side of a current transformer be grounded?
The principle of current transformer is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. A current transformer is composed of a closed iron core and winding. Its primary winding has very few turns and is connected in series with the line that needs to measure the current, so it often has all the current flowing through the line. The secondary winding has more turns and is connected in series with the measuring instrument and protection circuit. When the current transformer is in operation, its secondary circuit is always closed, so the impedance of the measuring instrument and protection circuit series coil is very small, and the working state of the current transformer is close to a short circuit. A current transformer is used to measure by converting the high current on the primary side into a low current on the secondary side, and the secondary side must not be open circuited.
1 Transformers classified by purpose
1. According to different purposes, current transformers can be roughly divided into two categories:
2. Measuring current transformer (or measuring winding of current transformer): provides current information of the power grid to measuring, metering and other devices within the normal operating current range.
3. Protective current transformer (or protective winding of current transformer): In the event of a power grid fault, it provides power grid fault current information to relay protection and other devices.
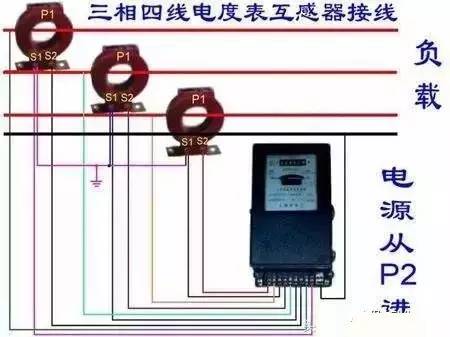
Wiring diagram of current transformer
2 Secondary grounding of transformer
1. The secondary grounding of a transformer refers to the grounding of the S2 terminal of the current transformer or the n terminal of the voltage transformer.
2. As long as a single point is grounded, due to the isolation between the secondary and primary windings of the transformer, there is no potential relationship between the secondary winding and the ground before grounding. After grounding, the transformer will not form a circuit with the ground, and during normal operation, the current will not flow to the ground.
3. When the insulation between the primary winding and the secondary winding is damaged, the primary high voltage is connected in series to the secondary circuit, and there is a fixed potential relationship between the primary high voltage and the ground. Current will flow to the ground and clamp the secondary voltage of the transformer to the ground voltage to ensure the safety of the secondary instrument and personnel.
3 Grounding reasons for the secondary side of voltage transformers and current transformers
1. There should be a grounding point on the secondary side of the voltage transformer, mainly for safety reasons. When the insulation between the primary and secondary windings is broken down by high voltage, the high voltage on the primary side will jump to the secondary side. With the grounding on the secondary side, it can ensure the safety of personnel and equipment. In addition, by grounding, phase voltage can be provided to the insulation monitoring device.
2. The secondary side of the current transformer should have a grounding point. Due to the high voltage on the primary side of the high-voltage current transformer, when insulation damage occurs between the first and second coils, high voltage will enter low voltage. If there is a grounding point on the secondary coil, high voltage will be introduced into the ground, keeping the secondary coil at ground potential, thereby ensuring the safety of personnel and equipment.