What is the function of a current sensor - accurate detection - [Vicwei]
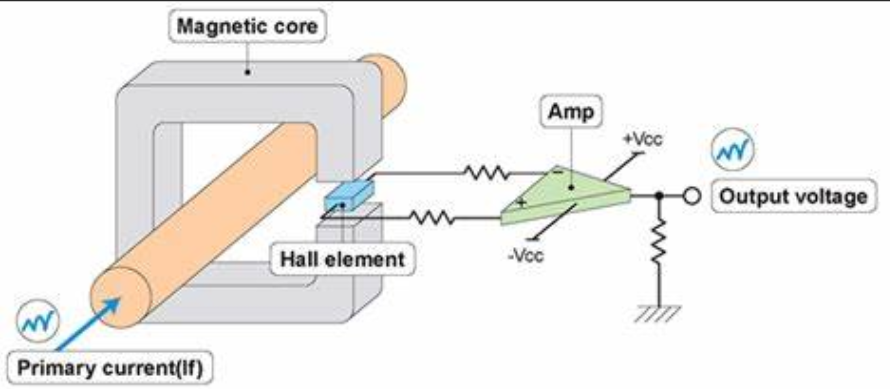
A Hall sensor is a special type of Hall current sensor with multiple turns on the primary side.What is the function of a current sensorWell, we know that the Hall effect is a product of electromagnetic effects, which refers to the deviation of charge carriers when current passes through a conductor perpendicular to the external magnetic field. An additional electric field is generated perpendicular to the direction of the current and magnetic field, resulting in a potential difference at both ends of the conductor. Sensors made using this principle for various purposes are called Hall current sensors. One of the basic construction principles of the Hall voltage sensor and Hall current sensor made using the Hall effect (closed-loop Hall current sensor) is shown in the following figure:
When the magnetic flux generated by the current is concentrated in the magnetic circuit through a high-quality magnetic core, the Hall element is fixed in the air gap to detect the magnetic flux. The reverse compensation current is output through a multi turn coil wound around the magnetic core to cancel out the magnetic flux generated by the primary side, so that the magnetic flux in the magnetic circuit always remains zero. After special circuit processing, the output terminal of the sensor can accurately reflect the current changes of the primary current.
Communicating with the engineers at Weikewei, there is currently relatively little explanation about the sensor pressure sensor. It can only be said whether the sensor outputs current or voltage. The sensor converts analog signals (such as pressure) into corresponding digital signals (voltage or current), and we determine the current pressure based on the corresponding relationship by reading these digital electrical signals. A pressure of 0-35MPa corresponds to a current of 4-20mA, or a pressure of 0-35MPa corresponds to a voltage of 1-5V. The working principle of voltage transformers and current transformers. Transformers are mainly divided into two types in power supply and distribution systems: voltage transformers and current transformers. In power supply and distribution systems, high currents and high voltages cannot be measured directly with ammeters and voltmeters, and must be measured by proportionally reducing the transformer. The internal structure of a transformer is a transformer. Operate according to the principle of a transformer. The working principle of a voltage transformer is equivalent to a transformer with an open circuit on the secondary side, used for voltage transformation. A voltmeter is connected to the secondary side to measure the voltage (multiple voltmeters can be connected in parallel). The secondary side of the voltage transformer cannot be short circuited. The working principle of a current transformer is equivalent to a transformer with a secondary short-circuit, used for current conversion. An ammeter is connected to the secondary side to measure the current (multiple ammeters can be connected in series). The secondary side of the current transformer cannot be open circuited. A voltmeter is equivalent to a measuring device for high load (high impedance) voltage transformers. An ammeter is equivalent to a small load (low impedance) measuring device for current transformers.
58彩票If you have more information to confirm and discuss, Weikewei's engineers can have face-to-face communication and response with you.